Successfully encapsulates anti-cancer agent in newly invented liposome High tumor shrinking effects and synergistic effect with an immune checkpoint inhibitor were observed
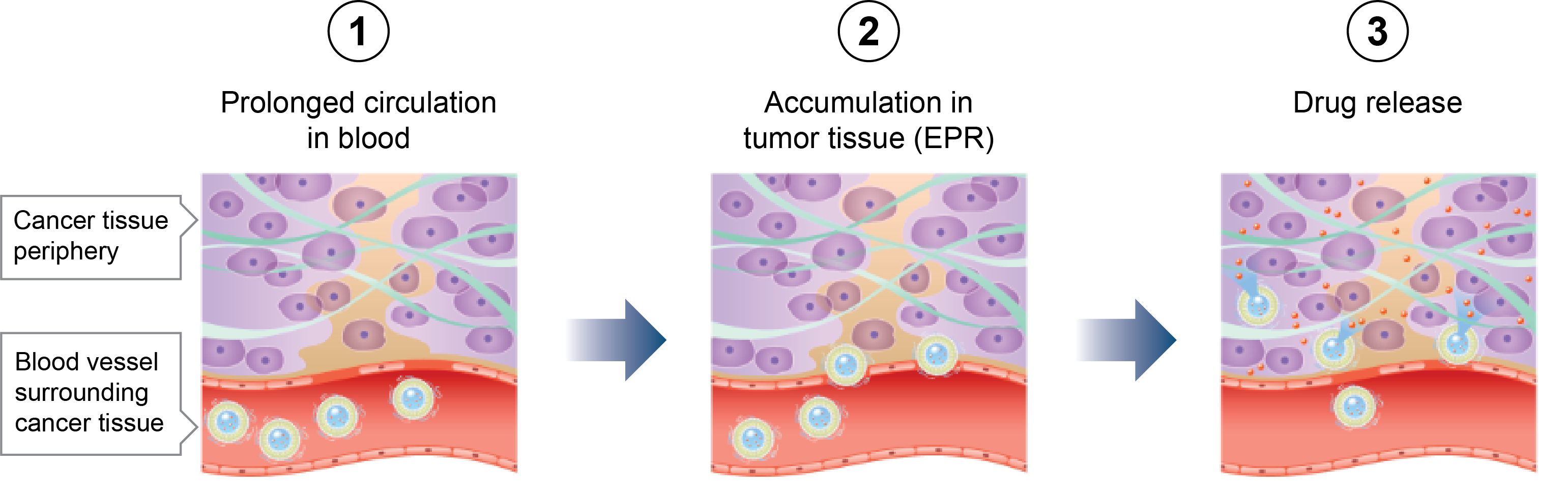
Fujifilm conducts research and development on the potential use of encapsulating drugs in liposomes, artificially constructed vesicles made from organic phospholipids that make up cellular membranes, by harnessing its advanced nano-dispersion technology, analysis technology, and process technology cultivated through its wide range of product development. In another study the liposome drug candidate FF-10832, which encapsulates the anti-cancer agent gemcitabine*3, has been observed to protect gemcitabine from eliminationand demonstrate an enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect*4 by which the FF-10850 accumulates within tumor and releases gemcitabine. A Phase I clinical trial of FF-10832 is underway in the U.S.
Topotecan has an extremely short half-life*5 in the blood, and also has the issue of causing serious bone marrow suppression*6 as a side effect in more than 80% of patients. A liposome drug where topotecan is encapsulated can be considered as a way to resolve these issues; however, topotecan has a tendency to pass through the liposome membrane, resulting in a problem where topotecan would leak into the blood before reaching the tumor. By enhancing the strength of the liposome membrane with the addition of new materials to the liposome ingredients, Fujifilm has succeeded in stably encupsulating topotecan. Fujifilm is conducting research on the drug as a candidate anti-cancer agent (development number: FF-10850), and has obtained the following results in studies in mice.
[Research Result 1] High tumor shrinking effects confirmed with monotherapy
(1) Experiment:
Mice with transplanted human-derived ovarian cancer cells (ES-2) were administered with topotecan and FF-10850, respectively, and the efficacy and tolerability were confirmed for each dosage. The period of administration was five consecutive days for topotecan and two cycles of one administration per week for FF-10850.
(2) Results:
・With topotecan, efficacy was observed with 30mg/m2 (6 mg/m2× five times), while with FF-10850, efficacy was confirmed with 3mg/m2 (1.5 mg/m2×twice). When the two drugs were compared, FF-10850 demonstrated efficacy that was greater than or equal to topotecan with 1/10 of the total dose of topotecan.
・With FF-10850, tumor shrinking effects were seen with 8 mg/m2 (4 mg/m2×twice). Furthermore, the relative body weight change which is an indicator of tolerability, was less than that of topotecan.

Based on the above, FF-10850 is expected to have high pharmacological efficacy that exceeds that of topotecan while maintaining tolerability even when dosage is increased.
[Research Result 2] Improved pharmacological efficacy observed when administered in combinationwith an immune checkpoint inhibitor
(1) Experiment:
Monotherapies and combination therapy with an immune checkpoint inhibitor*2 and FF-10850 was conducted on mice transplanted with mouse-derived colorectal cancer cells (CT26), and efficacy and tolerability were confirmed. The period of administration was three cycles of two administrations per week for the immune checkpoint inhibitor (30 mg/m2) and three cycles of one administration per week for FF-10850 (6 mg/m2).
(2) Results:
・When administered as a monotherapy, the median value for mouse survival time was 19 days for the immune checkpoint inhibitor and 27.5 days for FF-10850. Meanwhile, when administered as a combination therapy, the median value for mouse survival time exceeded 40 days, demonstrating a statistically significant difference when compared with the monotherapies. Mouse survival rates for the combination therapy were 75% at 40 days after administration, which was higher than the monotherapies.
・Even when administered as a combination therapy, noticeable side effects such as weight loss were not observed, and there were no issues with tolerability.

Based on the above, FF-10850 is expected to further suppress tumor proliferation through administration with an immune checkpoint inhibitor and prolong survival time.
Fujifilm will present its research results on FF-10850 at the “30th EORTC-NCI-AACR SYMPOSIUM”, one of the world’s most prominent cancer related conferences, to be held in Dublin, Ireland from November 13th to 16th, 2018.
Fujifilm is harnessing its advanced technologies such as the nano-dispersion technology and ability to synthesize and design compounds to undertake the development of new drugs in the key areas of cancer, central nervous system diseases, and infectious diseases. The company is also focusing on developing drug delivery system (DDS) technologies including liposome drugs, undertaking research and development to apply DDS technologies not only to low-molecular-weight drugs but also to next-generation drugs such as nucleic acid drugs and gene therapy drugs. Going forward, the company will contribute to the resolution of social issues by developing and delivering innovative, high value-added pharmaceutical products.
*1An anti-cancer agent (generic name: topotecan, product name: Hycamtin) developed by GlaxoSmithKline plc. Currently, the drug is distributed by Novartis. It is used as a treatment for ovarian cancer, small-cell lung cancer, and cervical cancer.
*2The general term for drugs that have an effect by enabling activated immune cells to attack cancer cells by inhibiting the mechanism (immune checkpoints) that weakens the action of immune cells. Widely used in the treatment of malignant melanomas, lung cancer, stomach cancer, and kidney cancer. The immune checkpoint inhibitor used in the combination therapy with FF-10850 was an anti-PD-1 antibody.
*3An anti-cancer drug (generic name: gemcitabine, product name: Gemzar) developed by the U.S. company Eli Lilly and Company. It is used as a drug of first choice for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, and is also indicated for the treatment of a wide range of other cancers (such as lung cancer and ovarian cancer).
*4As they grow, tumors generate surrounding blood vessels, but these newly generated blood vessels are not fully developed and have large gaps that are much smaller in normal blood vessels. When liposomes and polymers are retained within the blood, they do not permeate the walls of normal blood vessels, which have small gaps, permeating only the vascular walls around the tumor. In addition, as lymphatic vessels are not fully developed in tumors, the liposomes and polymers that have permeated are not easily eliminated, resulting in the accumulation of these liposomes and polymers in the tumor. This is called the EPR (enhanced permeability and retention) effect.
*5The time required for the concentration of a drug in the blood to be reduced to half.
*6The state where production of white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells in the bone marrow is reduced, leading to increased risk of infection and bleeding and symptoms such as anemia.
For inquiries on information in this media release, contact:
(Media Contact)
Corporate Communications DivisionTEL: +81-3-6271-2000
(Other Inquiries)
Pharmaceutical BusinessTEL: +81-6271-2171
###